Introduction
In three components of cloud operations, automation is required:
- Install and manage - Deliver infrastructure as code that is repeatable and consistent.
- Response - To diagnose and respond to issues, create event-based automation.
- Orchestrate - Use Azure or third-party services and solutions to orchestrate and integrate your automation.
Azure Automation is a cloud-based automation, operating system update, and configuration solution that allows you to manage your Azure and non-Azure environments consistently. Process automation, configuration management, update management, shared capabilities, and heterogeneous features are among the features included.
Various Azure services can meet the aforementioned objectives, each with its own set of characteristics and a function as a programmable platform for cloud solution development. Azure Bicep and Resource Manager, for example, provide a language for creating Azure resource deployment templates that are repeatable and consistent. Azure Automation can use that template to install an Azure resource and then perform a set of configuration actions afterward.
The Azure AD user account must be added to a role with permissions comparable to the Microsoft Owner position before you can create an Automation account. Resources for automation.
Step 1
Follow these steps.
Go to the Azure portal.
Log in to the Azure portal with an account that is a Co-Administrator of the subscription and a member of the subscription Administrator role.
Choose the Create a Resource option.
Type Automation. In the search results, select Automation.
On the Basics tab, fill in these details
- Subscription: Choose the Azure subscription account
- Resource group: Choose an existing resource group or create a new one.
- Automation account name: type name that is unique from its location and resource group.
- Region: Choose a region for the account.
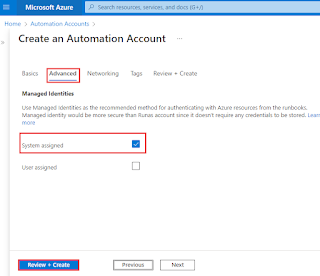
The Advanced tab option for your new Automation account can be configured on the Advanced tab. After the Automation account is created, you can additionally specify the user-assigned managed identity option.
Managed identities can be enabled later, and the Automation account will be established without one. See Enable managed identity to enable a managed identity once the account has been created. Select the Add user-assigned identities option for the user-assigned identity if both options are selected. Select a subscription and one or more user-assigned identities produced in that subscription to assign to the Automation account on the Select user-assigned managed identity screen.
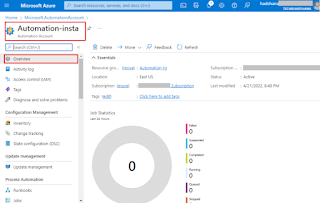
After that, Click Review + Create. You can view the result. And see the overview.
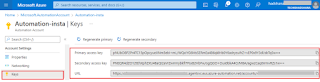
The Keys can be viewed, however, they are only used for registering DSC nodes and hybrid workers.
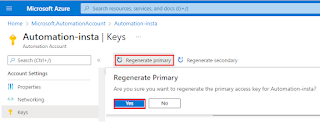
To keep the Automation account secure, you rotate your access keys on a regular basis. You can rotate your access keys using the Azure portal because you have two.
Next, we'll look at how to manage an Azure Automation Run As account.
Summary
In this article, I showed you how to create Azure Automation in Azure.





0 Comments